As the digital landscape continues to evolve at a rapid pace, businesses face an increasingly complex array of cyber threats that can compromise their data, systems, and operations. To stay ahead of these threats, organisations need to adopt and continually update a set of best practices for cybersecurity. We will navigate through a comprehensive view of these practices, expanding on each area with practical examples.
Core Cybersecurity Best Practices.
Implement A Multi-Layered Security Strategy
Defence in depth is a security philosophy that advocates for multiple layers of defence measures to protect against cyber threats. For instance, a company might have firewalls to block unauthorised access, intrusion detection systems to identify potential threats, data encryption to protect sensitive information, and regular security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities. The Bank of America, for instance, employs a defence-in-depth approach, combining preventative measures, robust detection systems, and a swift response strategy to manage cyber threats.
Regularly Update And Patch Systems.
Cyber threats often target vulnerabilities in outdated systems and software. Therefore, businesses should prioritise regular updates and patches to their systems, software, and devices. Microsoft, for example, releases regular patches to its software to address potential security vulnerabilities, ensuring that their customers have the most secure version of their product.
Use Strong Access Controls.
Businesses should establish strong access controls to prevent unauthorised access to their systems and data. These can include multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and regularly updated access rights. Google, for example, employs two-factor authentication, ensuring that only the authorised user can access their account, even if their password has been compromised.
Encrypt Sensitive Data.
Encryption is critical for protecting sensitive data, whether it’s at rest or in transit. Businesses should employ robust encryption standards and ensure the secure management of encryption keys. WhatsApp, for example, uses end-to-end encryption to ensure that only the sender and receiver of a message can read its content.
Conduct Regular Security Audits.
Regular security audits can help businesses identify potential vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of their security controls. These audits should include both technical assessments and reviews of policies and procedures. IBM, for instance, offers security audit services that assess an organisation’s current security posture, identifies gaps, and recommends improvements.
Train Staff In Cybersecurity.
Human error is often the weakest link in an organisation’s cybersecurity chain. Thus, businesses must invest in regular cybersecurity training for all employees. IBM, for example, provides its employees with annual cybersecurity training to ensure they are up-to-date on the latest threats and security practices.
Develop A Cyber Incident Response Plan.
Despite best efforts, cyber incidents can occur. Businesses need a response plan that outlines the steps to take during a cyber incident. This includes identifying the issue, containing the threat, eradicating the cause, and recovering systems and data. Companies like Uber have learned from past incidents and have since developed and implemented robust incident response plans.
Comply With Relevant Standards And Regulations.
Depending on the industry and jurisdiction, businesses must comply with a range of cybersecurity standards and regulations, such as the ISO 27001 for information security management, or regulations like the GDPR in the EU. For example, companies operating in the EU, like Facebook, must comply with GDPR requirements, which include provisions for data security and breach notification.
In understanding and implementing these best practices, businesses can fortify their cybersecurity posture, protect their assets, and build trust with customers and partners in the cyber domain.

Expanded Best Practices In Cyberspace For Businesses
The implementation of cybersecurity best practices extends to different components of the digital landscape.
Physical Infrastructure.
Businesses need to secure their physical infrastructure, such as data centres and network equipment, from both physical and cyber threats. Google, for example, ensures its data centres are secure from physical intrusion with layers of security measures like fences, security personnel, and surveillance cameras.
Multimodal Global Networks.
Companies need to ensure that their networks are secure and resilient. They should use secure network protocols, implement network segmentation, monitor network traffic, and ensure redundancy and failover capabilities. For instance, Amazon Web Services provides its customers with tools to monitor and secure their network traffic, detect anomalies, and withstand failures.
Servers.
Servers should be hardened against potential threats. This can involve measures such as disabling unnecessary services, using secure configurations, regularly updating and patching server software, and monitoring for signs of suspicious activity. Netflix, for instance, constantly monitors its servers and has automated systems in place to detect and respond to suspicious activity.
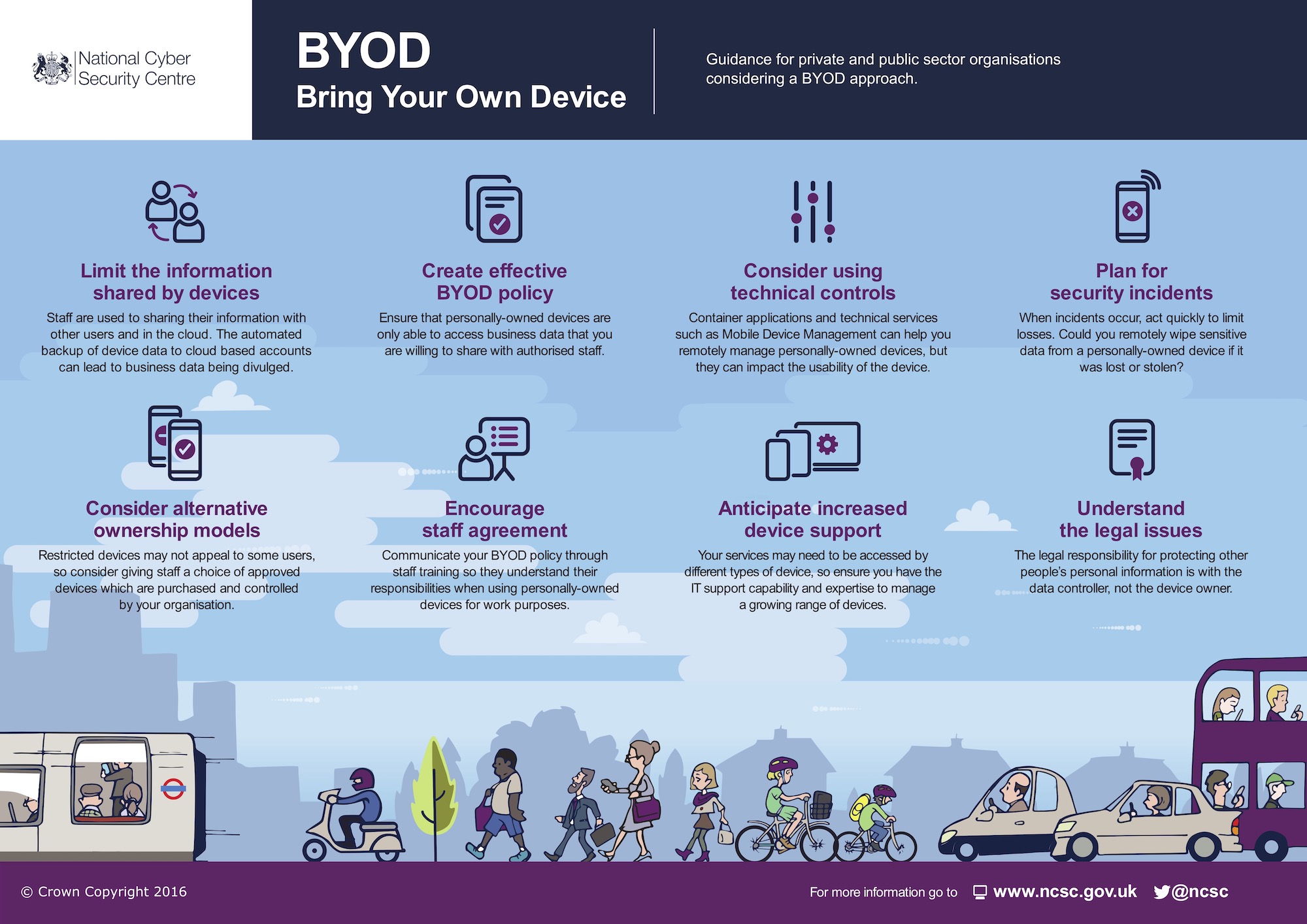
Personal Devices.
As remote work increases, personal devices used for business must be secure. Businesses should have a robust BYOD policy with requirements for device encryption, secure authentication, and up-to-date antivirus software. IBM, for example, has a comprehensive BYOD policy that includes mandatory device security measures and regular security checks.
Data Management.
Robust data management practices are essential to protect data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. This includes data classification, encryption, secure storage and transmission, and regular data backups. Companies like Salesforce prioritise data management practices to protect their customers’ data from breaches and ensure its integrity and availability.
Sector-Specific Considerations.
Different sectors have unique cybersecurity considerations based on their distinct needs and challenges. Military organisations need to protect sensitive information and operational integrity with secure communications, robust access controls, and advanced threat detection capabilities. Scientific organisations often handle large volumes of data, requiring robust data management practices, secure data sharing mechanisms, and strong data integrity controls. Government organisations need to ensure the protection of sensitive citizen data and the availability of critical services with robust data protection practices and secure online services.
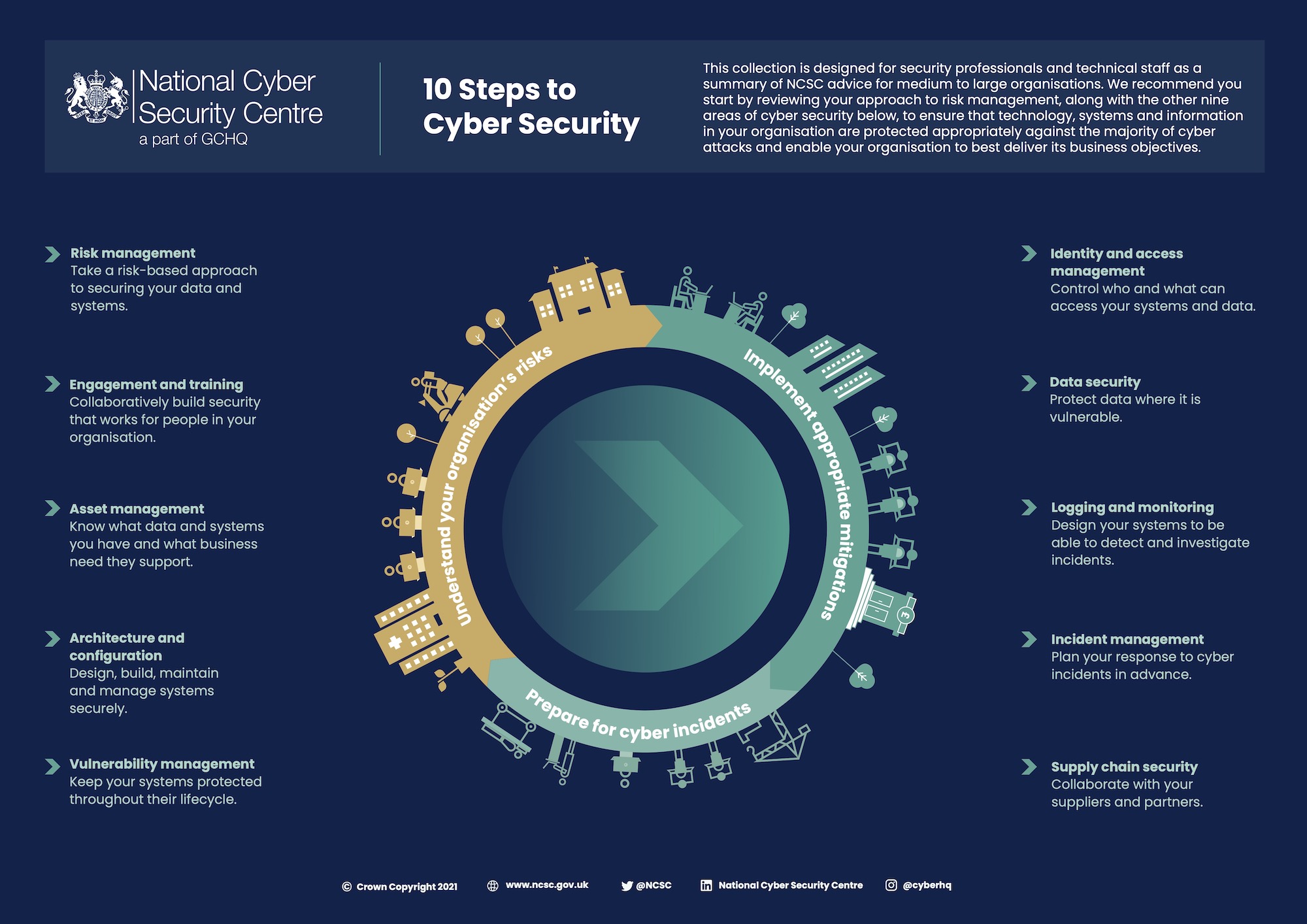
Incorporating Business Process And IT Service Management Perspectives On Cyber Best Practices.
Business And Operations Continuity.
Business continuity planning is critical to ensure that essential functions continue during and after a cyber incident. Microsoft, for example, employs strategies that aim to maintain or quickly restore operations, ensuring that their services remain available to customers even during an incident.
Disaster Recovery.
Disaster recovery focuses on restoring IT infrastructure and systems after a cyber incident. This involves data backups, system redundancy, and use of disaster recovery sites. Companies like Amazon Web Services provide disaster recovery solutions that allow businesses to quickly recover their systems and data following an incident.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) And Recovery Time Objective (RTO).
RPO and RTO are key metrics in disaster recovery planning. Netflix, for example, has clear RPO and RTO metrics in place that guide their disaster recovery strategies, ensuring the rapid recovery of services following a disruption.
IT Service Management (ITSM) Standards.
ITSM standards, such as ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), provide a framework for managing IT services, including cybersecurity. ITIL compliance demonstrates to stakeholders that a business takes cybersecurity seriously. Large corporations like IBM adhere to ITSM standards to guide their effective cybersecurity practices.
Regular Audits And Reviews.
Regular audits and reviews can help businesses assess the effectiveness of their cybersecurity practices and identify areas for improvement. Google, for example, regularly reviews its security practices and learns from each incident to continually improve its defences.
Employee Training And Awareness.
Regular training and awareness programs help employees understand their role in protecting against cyber threats. Intel, for instance, emphasizes the importance of each employee’s role in maintaining the company’s cybersecurity posture through regular cybersecurity awareness training.
By incorporating these additional best practices, businesses can ensure operational resilience and be prepared to respond effectively to cyber incidents, thus protecting their assets and ensuring the continuity and resilience of their operations in the face of cyber threats. The cyber landscape may be continuously evolving, but with a comprehensive and up-to-date set of best practices, businesses can navigate it with confidence.